Osteoarthritis of the hip joint, also called coxarthrosis, is one of the most serious diseases of a modern person, often leading to disability. Its first manifestations, mild pain in the groin, are generally ignored. The patient seeks qualified medical help, as a rule, when drug treatment is ineffective and stents are required.
Reasons
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint occurs due to a combination of various unfavorable circumstances. Microtrauma and full-blown injuries account for about a fifth of the total number of patients (on average 10-20%).
Other causes of hip osteoarthritis include:
- Excessive loads.
- Heart attack or aseptic necrosis of the hip joint.
- Prolonged stress, prolonged depression.
- Overweight.
- Inheritance.
- Congenital anomalies and underdevelopment.
- Inflammatory processes in the joints.
- Hormonal background failure.
Excessive loads
Until recently, it was believed that excessive physical exertion, long hours of walking, hard work (as a loader) is the main cause of osteoarthritis. But it's not like that.
A healthy joint, which has never been injured, perfectly tolerates any stress, especially at a young age, and nothing happens to it.
But if ever, even in childhood, there were microtraumas, then that joint is a candidate for the development of coxarthrosis. For this reason, the disease occurs in 20-30% of cases.
Heart attack
This is a violation of blood flow in the joint. In other words, the disease is called aseptic necrosis of the hip joint, which usually occurs after injury.
In addition to injury, the cause of a heart attack can be:
- Excessive alcohol consumption.
- Frequent corticosteroid injections.
- An unexpected shock (severe stress).
- Excessive single charges at a time when a person is not ready for them.
Heart attack becomes one of the causes of morbidity from coxarthrosis quite frequently, in 10-30% of cases.
Persistent stress
Few people believe in psychosomatics. However, prolonged experiences, depression, lack of understanding in the family and the various phobias that arise in this context are a direct path to problems in the joints, and not only in the hip. The incidence of osteoarthritis for this reason is very high, up to 50.
The mechanism for triggering disease in this situation is simple. During prolonged depression, the patient's body produces stress hormones that belong to the group of corticosteroids. The longer a person is in this state, the higher its concentration in the blood. Corticosteroids inhibit the production of hyaluronic acid, which is the main component of joint fluid. If not enough is produced or its composition is changed, the cartilage is poorly moistened, dries out and becomes covered with a mesh of small cracks.
The stress hormone reduces capillary permeability while affecting blood circulation in the joints.
Overweight
It is an additional factor among other causes of osteoarthritis of the hip joint (coxarthrosis).
Overweight people put enormous pressure on the joints, especially the ankles, knees and hips.
As long as they are young, everything seems to work within normal limits. But with age, maintaining the same weight, joint problems will snowball.
Inheritance
If one of your family members has had osteoarthritis, you don't need to get sick too. However, the appearance of "sores" is influenced by the peculiarities of metabolism, the structure of cartilage and can be inherited. This also includes the weakness of the muscular apparatus. For this reason, coxarthrosis can only be won in 10% of cases. And it is far from the fact that this happens. The main thing is to undergo periodic examinations and monitor the condition of your joints.
Congenital anomaly
This is usually treated in early childhood, allowing the child to grow and use the limb normally. However, the presence of an abnormality is always a risk for coxarthrosis, especially if you do not control the condition of your joints. The incidence rate is small, only 5. It should not be ignored that only a complex of several reasons leads to the appearance of arthrosis of the hip joint.
Joint inflammation
This process is commonly known as arthritis. The disease causes the appearance of secondary coxarthrosis in 2-3% of cases. The inflammatory process changes the quality of the intra-articular fluid. It becomes more viscous and stops performing its direct functions. As a result, the cartilage rubs against the cartilage, gradually collapsing.
Among other reasons, which directly or indirectly affect the appearance of coxarthrosis, can be named hormonal changes in menopause, metabolic diseases (diabetes), nervous diseases (in which the sensitivity of the lower extremities is lost), osteoporosis.
Symptoms
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint manifests itself in different ways. At the first stage of the development of the patient's pathology, almost nothing bothers, except weak, unpleasant, sometimes painful sensations, which pass independently.
The symptoms of osteoarthritis of the hip joint are specific and allow a preliminary conclusion (to make a diagnosis) already at the examination stage:
- Pain in the groin. This is the main symptom of the disease. If you feel during movement that something is wrong in this area, try to visit a doctor as soon as possible. Groin pain usually travels along the front or side of the thigh and can radiate to the buttock or knee. It is extremely rare for pain in osteoarthritis of the hip joint to reach the middle of the calf muscle. The patient feels discomfort when sinking into a chair or getting up, or after a long walk.
- Restricted mobility. This symptom indicates that osteoarthritis of the hip joint (coxarthrosis) is already progressing. If you ask a patient to “straddle a chair, ” that is, the other way around, it is unlikely that they will be able to do so.
- Cracking of the hip joint when walking. It does not appear immediately, but as osteoarthritis and cartilage destruction progresses. Its difference from the usual crunch of a healthy joint is a rather dry sound and a pain syndrome of weak or moderate intensity.
- Shortening of the diseased limb. It occurs when the disease is sufficiently advanced.
- Limping, falling on a sore leg due to total or partial destruction of the cartilage.
- Muscle atrophy of the affected leg. Visually it looks dry and unhealthy.
- Pain in the knee joint due to muscle atrophy.
Diagnosis
This moment is not too long for the patient. After a visual examination and questioning of the patient, the doctor prescribes a referral for blood donation: general analysis, biochemistry and rheumatic test. This is done to exclude the inflammatory process in the body. With osteoarthritis, all indicators are close to normal.
The next step is the instrumental exams:
- X-rays and / or CT.The CT scan shows the joints a little better.
- MRI. Named first. This survey is as informative as possible.
- Ultrasound of the joints.A sign of coxarthrosis in this study is a clear thinning of the cartilage. However, the accuracy of the result largely depends on the qualifications of the specialist who deciphers the obtained data. Therefore, to establish the disease, it is prescribed in rare cases.
Consequences
If osteoarthritis of the hip joint is not treated, in the hope that it "might go away on its own", the disease will actively progress. The consequences of such indifference to oneself are expressed in muscle atrophy and a clear shortening and drying of the diseased limb, at some point a person will not be able to move independently. The pain syndrome will become a constant companion of that patient; even strong pain relievers cannot relieve it. The only way out of this situation will be a joint replacement operation - endoprosthesis.
If coxarthrosis is diagnosed in an elderly patient, treatment should be started immediately. A sedentary way of life, which always arises in a patient due to constant severe pain, significantly shortens life.
Traditional treatment
It can be classified as medicinal and surgical. The second is used in the event that the first does not produce a significant improvement with prolonged use.

Early stage coxarthrosis is quite treatable:
- Medications.
- Manual therapy.
- Traction on a special table.
- With PIR (post-measurement relaxation).
- Therapeutic massage.
- Hirudotherapy.
- Recovery gymnastics.
Medications
The task of drugs is multifaceted. Not only tablets are used, but also ointments, intra-articular injections. Tablets (capsules, sachets) are prescribed to relieve pain (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), improve cartilage nutrition and improve the quality of intra-articular lubrication (chondroprotectors), relieve muscle spasm (muscle relaxants).
Ointments and creams have the weakest effect and are used to heat and irritate. Its effect is close to placebo. At the time of rubbing, the patient's body produces endorphins, pleasure hormones, which relieve pain quite effectively.
Intra-articular injections for osteoarthritis of the hip joint are very rare. This is due to the narrow joint space, which is quite difficult to get into, even with the use of special auxiliary equipment. The procedure is performed through the groin and is so complex that ninety-nine percent of physicians prefer to inject the drug into the periarticular sac by puncturing the side of the thigh.
By injection:
- Relieve high intensity pain syndrome (corticosteroids).
- They nourish the cartilage (chondroprotectors).
- Improves lubricant quality (hyaluronic acid substitutes - injected through the groin).
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are given by mouth for mild to moderate pain. They also effectively extinguish inflammatory processes.
Manual therapy
Treatment by an experienced specialist can help patients with moderate coxarthrosis to stand up. The task of the doctor is to restore the mobility of the joint, relieve pain. Manual therapy is subdivided into manipulation (a single effect on the joint) and mobilization (4 courses per year, 3 to 4 sessions each).
Mobilization allows you to stretch the affected limb with minimal pain. Enlarge joint space, relax tense muscles. Manipulation is only allowed in the early stages of the disease.
Traction on a special table also gives certain results, but loses significantly with manual therapy. The machine (device), unlike the doctor's hands, does not feel the patient and, if used incorrectly, can cause harm.
PIR
Post-isometric relaxation involves an active interaction between the patient and the treating physician. The meaning of the method is that the patient relaxes / tenses certain muscle groups as directed by a specialist. At this point, the doctor stretches your ligaments and joints.
This coxarthrosis treatment helps relieve muscle spasms. The method is effective for coxarthrosis of I and II degrees.
Massage
If you decide to use this method, you need to find a highly qualified specialist. Otherwise, instead of alleviating the condition, it may make it worse. The method is effective for grades I and II coxarthrosis as an auxiliary.
Massage for coxarthrosis should not be painful. The sensations during the procedure are pleasant, you should feel relaxation and comfort.
Please note that there are contraindications to massage. Don't self-medicate.
Hirudotherapy
Leech treatment helps in the early stages of osteoarthritis of the hip joints. The saliva of this worm improves blood circulation, the elasticity of cartilage, and contains many useful substances. It acts as a chondroprotector, only softer.
Leeches are placed not only on the sore thigh, but also on the sacrum, lower abdomen, and lower back. You need to complete 2 courses of 10 sessions per year.
Recovery gymnastics
No disease can be cured or alleviated without a dose of physical exercise. Osteoarthritis of the hip joint is no exception. If you do not strengthen the muscles, their atrophy is inevitable, while the condition of the cartilage will deteriorate twice.
It is preferable to study in special groups under the supervision of specialists. The medical complex is selected by a doctor based on the examinations, the degree of coxarthrosis and the physical abilities of the patient.
Endoprosthesis
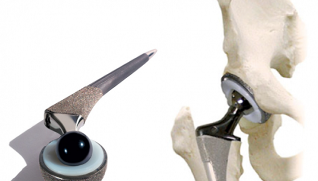
Surgical intervention is performed in grades III and IV of coxarthrosis, when conservative treatment gives minimal results or is not effective at all. The surgeon's task is to replace both the joint head itself and the acetabulum with artificial implants through a small incision in the thigh.
Now these operations are underway. To imagine what awaits you if you ignore the first signs of coxarthrosis, imagine the course of the operation (in short):
- The patient is anesthetized.
- An incision is made in the thigh, soft tissues are removed, and nerves are pushed.
- The joint is removed from its bed. In simple words, the doctor makes an artificial dislocation to remove your head.
- The head of the joint with part of the bone is removed.
- The acetabulum is cleaned.
- An endoprosthesis, an artificial joint head, is inserted into the bone, or rather, it is "blocked. "
- An artificial acetabulum is inserted.
- The joint is repositioned. The doctor checks your mobility by moving the limb in different directions.
- The wound is disinfected and sutured.
After the operation, a fairly long period of rehabilitation and adherence to a certain regimen are required.
Traditional methods
For lovers of self-medication, it should be noted that coxarthrosis is a disease that should only be treated by a doctor. All the popular methods in the form of rubs, lotions and other "unusual things" will not lead to anything good.
However, some recipes of traditional medicine can be used as auxiliaries of the first degree of the disease:
- Cabbage leaves.It is used to relieve pain without taking pain relievers and to relieve the "twisting" of the sore joint. In the evening, tie a few cabbage leaves to your thigh, after rubbing pure honey on the skin. Wrap it in plastic wrap and something warm. Remove the honey in the morning, rinse with cold water, and repeat the compress. Repeat until the pain goes away.
- Honey and turnip ointment.Similar in action to cabbage leaves. You just have to tinker to cook it. The ratio of turnip and honey is 1/1. Turn the root vegetable in a meat grinder, add honey, stir. Pour 50 ml of vodka or alcohol. Stir again. Rub into the affected joint until the pain goes away.
- Healing baths.For cooking, you need pine twigs (a couple of large twigs), turpentine (1 teaspoon), bath salt (1 kg), and washed Jerusalem artichoke tubers cut into pieces (3-4 pieces). Fill with hot water and let it rest. When the water is pleasant to take a bath, remove the branches and Jerusalem artichoke and begin the procedure. At the end, apply an iodine net to the sore thigh or rub with honey, put on something warm and go to bed.

Osteoarthritis of the hip joint is a serious disease that occurs when several causes are combined.
In order not to become disabled, do not wait for the consequences, get annual examinations, at the first feeling of discomfort in the groin area, consult a doctor.



































